
So consider using a LinkedHashMap when you want a Map with its key-value pairs are sorted by their insertion order.

This implementation also allows nulls like HashMap.

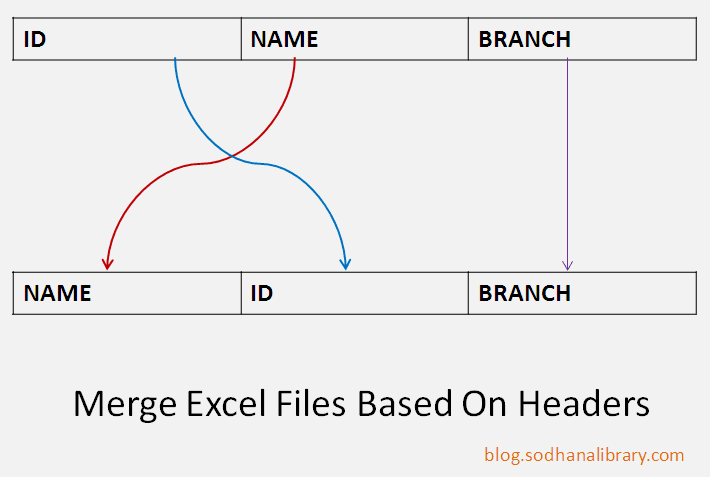
#Java merge method map code
This tutorial provides code examples around the three major implementations of Map which are described below. Each class (key) is associated with a list of students (value). Each manager (key) is associated with a list of employees (value) he manages. A map of error codes and their descriptions.
#Java merge method map update
Use Maps when you want to retrieve and update elements by keys, or perform lookups by keys. Why and When Use Maps:Maps are perfectly for key-value association mapping such as dictionaries. The order of a map depends on specific implementations, e.g TreeMap and LinkedHashMap have predictable order, while HashMap does not. Some implementations allow null key and null value ( HashMap and LinkedHashMap) but some does not ( TreeMap). Instead, it starts an independent branch in the Java Collections Framework, as shown in the following diagram: Characteristics of a Map:Because a Map is not a true collection, its characteristics and behaviors are different than the other collections like List or Set.A Map cannot contain duplicate keys and each key can map to at most one value. The following picture illustrates a map: Note that a Mapis not considered to be a true collection, as the Map interface does not extend the Collection interface. It models the function abstraction in mathematics. Overview of Map Collection A Map is an object that maps keys to values, or is a collection of attribute-value pairs.
#Java merge method map how to


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
